
What is an ultrasound, how does an ultrasound scan work, what does it show – and who should book a private ultrasound appointment?
An ultrasound scan is one of the most modern methods of examination. But what is ultrasound? It’s an imaging process that uses reflected sound waves to look at the body’s functions and abnormalities, without putting any strain on the body.
Almost every part of our body and every organ can now be examined and diagnosed by ultrasound, most commonly, but not exclusively, for example:
At our centre we also perform ultrasound scans of the abdomen, pelvis, joints, thyroid, neck and limb veins, soft tissue and breast. In our specialist examination rooms, we have ultrasound equipment for specialised use in the fields of urology, gynaecology, cardiology and liver disorders.

Anyone can request an ultrasound scan – or UH scan for short – as the procedure has no harmful effects on the body. You can request the scan without a referral, but if you have a referral from a specialist, you should bring it with you as the questions it asks will help the radiologist. Some ultrasound examinations are worth having annually for screening purposes, such as breast and lymphatic regions, prostate, vagina, pelvic area, heart, cervical soft tissue and cervical veins.

Of the ultrasound scans, the abdominal-pelvic ultrasound scan requires only preparation. A 4-6 hour meal break and urinary retention for approximately 1-2 hours prior to the scan is required for a complete evaluation. Prior to joint examinations, especially in the case of injuries, we recommend that an X-ray of the joint is taken prior to the examination to allow a more accurate diagnosis.

The examination of a region takes about 15-20 minutes, during which time the radiologist can discuss your complaints with you, answer your questions or refer you to another specialist, depending on his or her competence. The examination will be documented in images and in writing, which you will receive immediately after the examination.
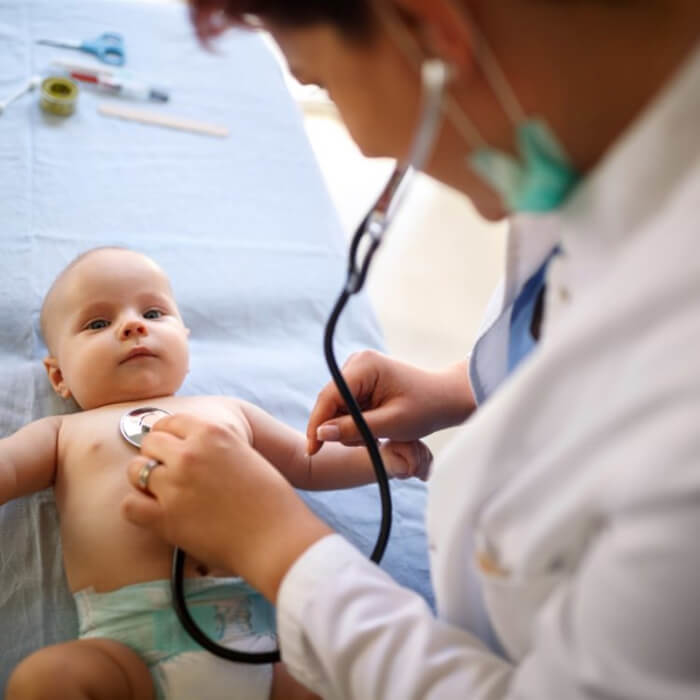
The ultrasound scan has no harmful effects on tissue, so it can be performed at any age. At our institute, we can examine both adults and children, and we can even perform abdominal examinations on babies.
Before the examination, the affected body part and its surroundings must be uncovered and the patient must be positioned on an examination bed in the position determined by the specialist (lying or sitting). The area is examined by the radiologist by placing and moving the so-called ultrasound head with an ultrasound gel on the area and applying slight/ sometimes slightly stronger pressure. The examination is painless. During this time, the specialist may ask you questions to get a more comprehensive picture of you.
Afterwards, the ultrasound gel can be wiped off and, if it gets on clothing, easily removed with water.

In our private ultrasound clinic, we have specialised ultrasound equipment for specialised use. We offer the following ultrasound examinations as part of a specialist examination or as a consultation at the ultrasound centre. Click here to find out more about ultrasound prices.
The abdominopelvic ultrasound scans take pictures of the internal organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, bladder, prostate, ovaries, uterus…) located between the diaphragm and the pubic bone. It can also be used to examine the lymph nodes and large abdominal blood vessels in this area. It is of limited value for the examination of the stomach and intestines, but is suitable for lesions permeating the intestinal wall. It can be used for periodic screening, to clarify the cause of abdominal and pelvic complaints, pains, urinary and menstrual problems. It has a role in the control and follow-up of existing, known lesions. The examination can detect abnormalities in the size and structure of the organs concerned, cysts, abscesses, stones, effusions, haemorrhages, benign and malignant lesions. Preparatory examination: 4-6 hours of fasting and 1-2 hours of urinary retention.
Cervical soft tissue ultrasound scans can examine the subcutaneous area of the neck, salivary glands, lymphatic glands, muscles, blood vessels and thyroid gland. It can be used for periodic check-ups, to investigate lumps and palpable lesions in the neck area, to find out the cause of painful swallowing problems, and in case of neck muscle injuries. It can also be used to control existing, known lesions or even after surgery. It can be used to detect inflammatory lesions, as well as benign or malignant lesions. For the assessment and follow-up of thyroid diseases / nodules / thyroid dysfunction, ultrasound is the test of choice. The carotid arteries, “carotid arteries”, can be used to assess the condition of the blood vessels using the so-called Color-Doppler technique. It is excellent for detecting vascular stenoses and determining the location of vascular calcifications.
The ultrasound examination of the soft tissue under the skin surface can be used to infer the presence of palpable nodules, the cause of pain, and the characteristics of muscle injuries and their bleeding.
Tests called Doppler/Colour Doppler are a technical method of examining blood vessels using general ultrasound. It provides information about the circulation and flow in the blood vessels. The technique is based on the reflection of ultrasound waves from the so-called “shaped elements” of the blood flowing in the vessel, and also allows the determination of the blood flow rate and volume in a selected cross-section of the vessel. It can be used in cases of smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, atherosclerosis, headaches, dizziness, visual problems, non-injury leg swelling, numbness in the limbs. In addition to blood vessels, the so-called power-Doppler method can also be used to examine the blood supply to low-speed circulations and even to various lesions in the area under examination.
Breast ultrasound examination includes physical and ultrasound examination of the breasts, axillary ducts, clavicle, sternum soft tissue area and lymph nodes. The basic, primary method of breast examination is X-ray mammography over the age of 35. Under 35 years of age, an ultrasound scan may be requested independently, but a mammogram may also be warranted if a lesion is found. The ultrasound scan may be used for periodic screening or in the case of breast complaints, lumps in or around the breast, problems/injuries related to breast implants. Dilatation of the milk ducts, inflammation of the glandular tissue, cysts, other benign or malignant tissue lesions, ruptures of breast implants can be detected.
 Dr. Anett Szomják
general radiologist
Hungarian, English
Doctors Hungarian, English language
Dr. Anett Szomják
general radiologist
Hungarian, English
Doctors Hungarian, English language
 Dr. Tímea Nagy
radiologist specialist
Hungarian, English
Doctors Hungarian, English language
18+
Patients 18+ from ages and up
Dr. Tímea Nagy
radiologist specialist
Hungarian, English
Doctors Hungarian, English language
18+
Patients 18+ from ages and up
 Dr. Andor Huszár
ultrasound and radiology specialist
Hungarian, English
Doctors Hungarian, English language
6+
Patients 6+ from ages and up
Dr. Andor Huszár
ultrasound and radiology specialist
Hungarian, English
Doctors Hungarian, English language
6+
Patients 6+ from ages and up
 Dr. Robin Badalay
radiologist specialist
Hungarian
Doctors Hungarian language
16+
Patients 16+ from ages and up
Dr. Robin Badalay
radiologist specialist
Hungarian
Doctors Hungarian language
16+
Patients 16+ from ages and up
 Dr. Lajos Jakab
chief radiologist
Hungarian
Doctors Hungarian language
10
Patients 10 from ages and up
Dr. Lajos Jakab
chief radiologist
Hungarian
Doctors Hungarian language
10
Patients 10 from ages and up
 Dr. Szilárd Szőke
radiologist specialist
Hungarian
Doctors Hungarian language
7+
Patients 7+ from ages and up
Dr. Szilárd Szőke
radiologist specialist
Hungarian
Doctors Hungarian language
7+
Patients 7+ from ages and up
 Dr. Krisztina Barna
radiologist
Hungarian, Swedish, English
Doctors Hungarian, Swedish, English language
10+
Patients 10+ from ages and up
Dr. Krisztina Barna
radiologist
Hungarian, Swedish, English
Doctors Hungarian, Swedish, English language
10+
Patients 10+ from ages and up